Abstract
Introduction: Hydroxyurea decreases many complications of sickle cell anemia (SCA) but is underused in treatment-eligible patients. Barriers to hydroxyurea initiation occur on the health care system, provider, and patient level. Novel strategies to increase hydroxyurea use in patients with SCA are needed. To address this challenge at our center, we implemented the Quick Start Hydroxyurea Initiation Project (Q-SHIP).
Methods: Patients with SCA were eligible to participate in Q-SHIP if they presented to the Children's National Health System (CNHS) emergency department (ED) for pain or acute chest syndrome and were not taking hydroxyurea. Patients <9 months old, on chronic transfusions, pregnant, or not followed by CNHS hematology were excluded. Eligible patients were referred to a weekly Q-SHIP clinic visit focused on hydroxyurea education and were offered initiating treatment at the visit's conclusion. Participants completed a pre-session questionnaire, discussed hydroxyurea with a hematologist using a handbook developed by CNHS, and watched videos featuring patients and parents of children with SCA sharing their experience with hydroxyurea. Subjects were classified as starting hydroxyurea if they had a clinic visit for hydroxyurea monitoring within 3 months of participation in a Q-SHIP session.
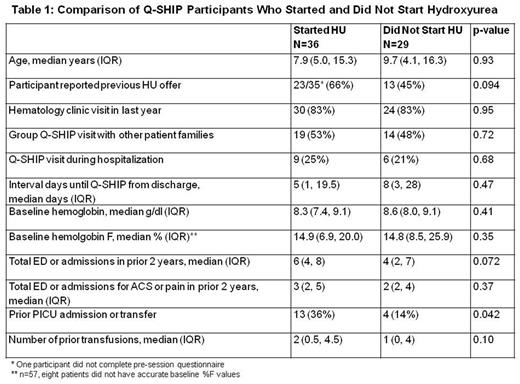
Results: Over 13 months (2/1/2016 - 3/31/2017) 65 eligible patients participated in Q-SHIP a median of 5 days (IQR 2, 20 days) after ED or hospital discharge. Although 44% (28/64) of participants reported no previous hydroxyurea offer, provider clinic documentation indicated that 61% (17/28) of these families had declined a previous hydroxyurea offer. After Q-SHIP, 55% (36/65) of participants started hydroxyurea. Subjects who started hydroxyurea after Q-SHIP were similar to those who did not, except subjects who started were more likely have a history of an intensive care unit admission (Table 1). After a median follow-up of 11 months, 81% (29/36) of participants who started hydroxyurea after Q-SHIP continued on therapy. Among Q-SHIP participants continuing treatment, mean corpuscular volume increased by a median of 8.6 fL (IQR +5.4, +17.7, p<0.0001) and hemoglobin F increased by a median of 5.8% (IQR +3.0, +11.3, p<0.001). One year after implementation of Q-SHIP, the proportion of treatment-eligible patients with SCA who presented to the ED with pain or ACS who were receiving hydroxyurea increased; February 2016: 56% (32/57) vs. February 2017: 73% (43/59), p=0.059.
Conclusion: Addressing indications for hydroxyurea therapy in a clinic encounter exclusively for this purpose soon after a SCA complication is a meaningful time to meet with families of children with SCA to initiate treatment.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal